Difference between revisions of "Support user level2"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{{Page_Introduction_Title}} | {{Page_Introduction_Title}} | ||
<!-- Transclusion : Intro Begin ------------------------------------------------------------------><section begin=intro /> | <!-- Transclusion : Intro Begin ------------------------------------------------------------------><section begin=intro /> | ||
| − | The supporter finds here instructions how to handle a user's level 2 telephony problems | + | The supporter finds here instructions how to handle a user's level 2 telephony problems: |
| + | :* Best Practice for Handling an User Problem | ||
| + | :* Record the Customer's Data and Problem Description | ||
| + | :* Analyzing the Customer Problem | ||
| + | :* Solving the Customer Problem | ||
<!-- Transclusion : Intro End --------------------------------------------------------------------><section end=intro /> | <!-- Transclusion : Intro End --------------------------------------------------------------------><section end=intro /> | ||
Revision as of 09:21, 18 September 2017
| Note | The features and/or parameters listed in this article may not be available from your telephone service provider. |
|
|
|
|
|
Introduction
The supporter finds here instructions how to handle a user's level 2 telephony problems:
- Best Practice for Handling an User Problem
- Record the Customer's Data and Problem Description
- Analyzing the Customer Problem
- Solving the Customer Problem
Contents
- 1 Introduction Support Level 2
- 2 Best Practice for Handling an User Problem
- 3 Record the Customer's Data and Problem Description
- 4 Cross Check the User Inputs
- 5 Check the Big Picture
- 6 Analyzing the Customer Problem
- 7 Solving the Customer Problem
- 7.1 Solve Problem: The User Device does not Register
- 7.2 Solve Problem: Incoming Connections are Failing
- 7.3 Solve Problem: Outgoing Connections are Failing
- 7.4 Solve Problem: Irregular Connection Release
- 7.5 Solve Problem: Disturbed Speech Transmission
- 7.6 Solve Problem: Disturbed FAX Transmission
- 7.7 Solve Problem: DECT Multi-Cell Handsets are not Working
Introduction Support Level 2
The level 2 support is the first instance where the user's telephony problems are handled that a user cannot solve himself. Additionally the level 2 supporter must be able to detect if the user problem is a "single" problem or if there is a large scale problem, that produces the same problem for multiple customers, e.g. data transfer problems in the Internet so that no VoIP call signaling is possible.
The level 2 supporter must be aware of the complexity of a VoIP system and the multitude of telephony solutions on the user side. Further he needs an understanding of:
- IP networking
- VoIP protocols SIP for signaling, SDP and RTP for speech transmission.
Overview of a VoIP system and the multitude of user telephony solutions:
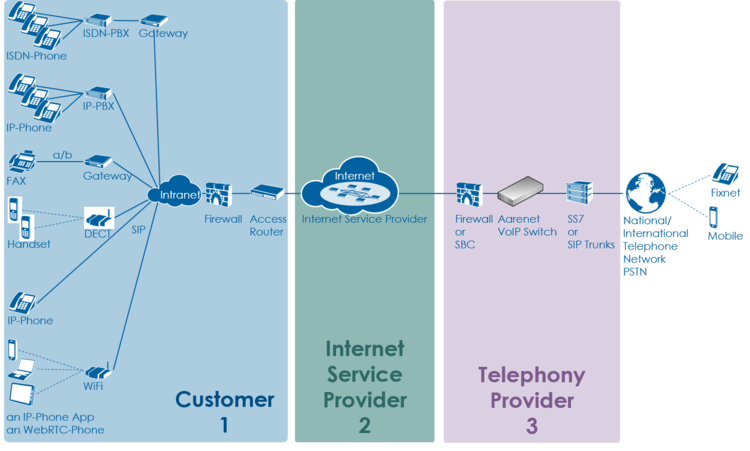
The level 2 supporter faces problems with the following layers:
- Equipment
- IP data transfer
- Telephony service
And each of this layer can be located into the following raw areas:
- Customer/User site
- Internet Service Provider ISP
- Telephony Provider
This layer and dividing into areas produces a "3x3 Support Matrix":
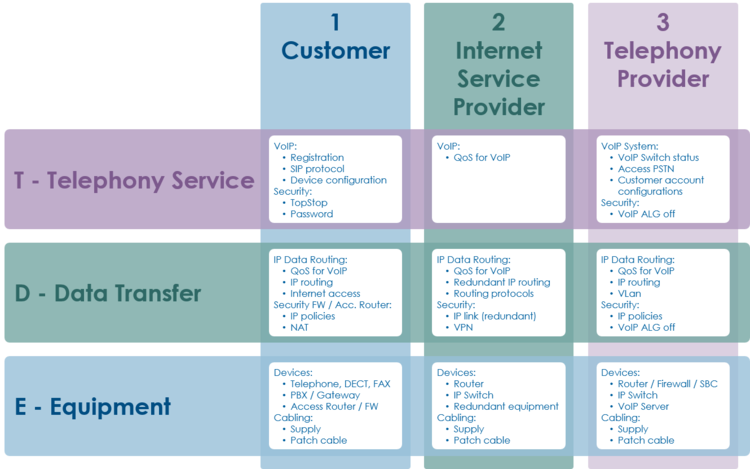
Within this "3x3 Support Matrix" the supporter can:
- advice the customer what to do when the problem is located in the nodes 1-T, 1-D and 1-E
- check the customer configurations on the VoIP Switch, node 3-T, and, if he has operator rights, adjust configurations.
For the other cases the level 2 supporter must be able to identify if:
- the user must contact his ISP, due to possible Internet access problems
- the VoIP System administrator must be involved, due to possible telephony service problems
- Hint:
- These cases indicate mostly large scale problems within the VoIP system!
Best Practice for Handling an User Problem
| Best Practice |
|
Record the Customer's Data and Problem Description
Get the Customer's Data
From the customer get:
- Name of the caller
- Telephone number of the caller
- if applicable the company name
Identify the Customer's Use Case
From the customer get if it is a:
- Residential user
- Business "Legacy ISDN PBX"
- Business "IP PBX with SBC"
- Business "SIP Trunk / IP PBX"
- "vPBX"
- etc
If the customer doesn't know then identify via the ConfigCenter the telephone number and its associated account.
Note the Customer's Problem Description
From the customer get:
- Date and time of the issue
- The involved telephone numbers
- The problem description
If the customer doesn't know then identify via the ConfigCenter the telephone number and its associated account.
Cross Check the User Inputs
With this cross check the supporter can validate the user information, gets an impression of the state of the account and will probably find the reason for the user problem...
Via ConfigCenter check the users status and account configuration on the VoIP Switch:
- Check the telephone number registration status.
- If there is no registration you can proceed directly with
 The user device is not registered ...
The user device is not registered ...
- If there is no registration you can proceed directly with
- Check "TopStop":
- Check if a TopStop in the account or address prevents the user from doing outgoing calls.
- Check "RuleSet":
- Check if a RuleSet in the account or address prevents the user from doing outgoing or receiving calls.
- Check "Call Forwards" or "Call Rejecting":
- Check if a "Call Forwards" or "Call Rejecting" in the account prevents the user from doing outgoing or receiving calls.
- Check "Call Data":
- Consult the "Call Data" for the last connection attempts and connections longer than 2min of the user.
Check the Big Picture
At this point the supporter should get aware if the problem is limited to this user or if it could be large scale problem within the VoIP System.
If the supporter suspects a large scale problem, due to a great amount of the same ore similar user complains then he should contact the telephony provider support or emergency organization.
If the supporter has enough privileges he can check:
- The VoIP Switch component status
- This will show if the VoIP Switch itself hat a problem.
- The VoIP System monitor
- Here you can check if:
- The registrations dropped in a large scale
- The calls dropped in a large scale
- The IP connectivity somewhere in the VoIP system failled
- Here you can check if:
At any rate the supporter must inform the VoIP system administrator!
Analyzing the Customer Problem
During this first step the supporter shall identify the user's problem.
By interviewing and checking the facts the supporter must be able to collect all basic information:
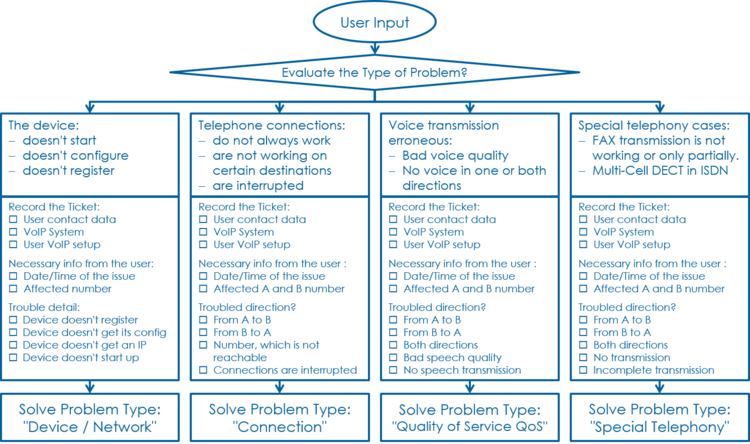
By identify the user's use case the supporter can selectively optimize the questioning.
Use Case "Residential" Questioning
Solving the Customer Problem
Solve Problem: The User Device does not Register
1 Check: Review the account and telephone number configuration
| Customer | Internet ISP |
Telephony Provider | |
| Telephony | Check via ConfigCenter:
Actions:
| ||
| Data Transfer | |||
| Equipment |
2 Check: Where REGISTER messages received from the device on the VoIP Switch?
| Customer | Internet ISP |
Telephony Provider | |
| Telephony | In the "Support Log" search for the device registration in the present and past time.
| ||
| Data Transfer | |||
| Equipment |
Failed registrations due to disabled account or address:
|
2017-09-15-07:56:49.553 Registration failed, disabled account aan1-00093 tried to register number 0449980010 |
Actions:
- Check why the account is disabled and activate if allowed.
Failed registrations due to wrong SIP credentials:
|
2017-09-15-08:05:38.117 Registration failed, invalid credentials for account acc-01 |
Actions:
- The user must manually adjust the SIP credentials on the device
- The user must re-configure the device via AdminCenter
The device didn't refresh its registration:
|
2017-09-15-07:59:00.862 RegID989961 ended for 0987654321 ip=111.111.111.111:65398 ua=my-device v1.0 |
Actions:
- Check if the device is really on-line! Device defect? power? patch? IP address? → see below
For information a successful registration:
|
2017-09-15-07:59:30.383 RegID989965 started for 0987654321 ip=111.111.111.111:65398 ua=my-device v1.0 |
Hint:
The supporter might try to find REGISTER messages from the device in the "Trace" . This gives the certainty that the message was received by the VoIP switch. The supporter can filter for the telephone number.
If the IP address is needed then the customer must be able to tell or evaluate it, e.g.:
3 Check: Is the device is correctly configured for registration?
| Customer | Internet ISP |
Telephony Provider | |
| Telephony | Check that the device has the correct configuration for:
Actions:
|
||
| Data Transfer | |||
| Equipment |
4 Check: Is the device is powered on, not defect, connected to the IP network?
| Customer | Internet ISP |
Telephony Provider | |
| Telephony | |||
| Data Transfer | |||
| Equipment | Is the device correctly powered?
Actions:
Actions:
|
5 Check: Has the device an IP address and can access the Internet?
| Customer | Internet ISP |
Telephony Provider | |
| Telephony | |||
| Data Transfer | Has the device got an IP address?
Actions:
|
||
| Equipment |
- Was the device registered in the past?
- Where outgoing and/or incoming calls possible in the past?
Solve Problem: Incoming Connections are Failing
Instruction how to solve failing incomming connections, e.g.:
- User device not correctly registered
- Wrong calling number
- User device not correct configured
Solve Problem: Outgoing Connections are Failing
Instruction how to solve failing outgoing connections, e.g.:
- User device not correctly registered
- Wrong called number
- User device not correct configured
Solve Problem: Irregular Connection Release
Instruction how to solve irregularly released user connections, e.g.:
- Failing Session Timer
Solve Problem: Disturbed Speech Transmission
Instruction how to solve disturbed speech transmission, e.g.:
- Short interruptions during the connection
- No transmission in one direction from the beginning of the connection
- No transmission in both directions from the beginning of the connection
Solve Problem: Disturbed FAX Transmission
Instruction how to solve interrupted FAX transmission, e.g.:
- Fax transmission doesn't start
- Not all pages are transmitted
Solve Problem: DECT Multi-Cell Handsets are not Working
Instruction how to solve problems with DECT Multi-Cell handsets, e.g.:
- Hand over from cell to cell not working
- Bad speech quality
© Aarenet Inc 2018
Version: 3.0
Author: Aarenet
Date: May 2017