|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{DISPLAYTITLE: User Support Level 2 }} | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE: Brief Tutorial of the SIP Signaling and SDP Media Protocols }} |
| | {{PAGE_HEADER}} | | {{PAGE_HEADER}} |
| | {{Page_Menu_List_Help_Support}} | | {{Page_Menu_List_Help_Support}} |
| Line 7: |
Line 7: |
| | {{Page_Introduction_Title}} | | {{Page_Introduction_Title}} |
| | <!-- Transclusion : Intro Begin ------------------------------------------------------------------><section begin=intro /> | | <!-- Transclusion : Intro Begin ------------------------------------------------------------------><section begin=intro /> |
| − | The supporter finds here instructions how to handle a user's level 2 telephony problems: | + | The VoIP Switch administrators, operators and supporters find here information about the Session Initiation Protocol SIP and Session Description Protocol SDP. |
| − | :* Best Practice for Handling an User Problem
| |
| − | :* Record the Customer's Data and Problem Description
| |
| − | :* Analyzing the Customer Problem
| |
| − | :* Solving the Customer Problem
| |
| − | <!-- Transclusion : Intro End --------------------------------------------------------------------><section end=intro />
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | __TOC__ <!-- Table of Contents -------------------------------------------------------------------->
| + | Basic knowhow about connection signalization with '''Session Initiation Protocol SIP''': |
| | + | :* [[ {{NAMESPACE}}:support_voip_protocol#SupportSipBasics | Basics about SIP Protocol ]] |
| | + | :* [[ {{NAMESPACE}}:support_voip_protocol#SupportSipResponseCodes | List of most important SIP Response Codes ]] |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | <!-- PAGE BREAK --> <!-- PDF Creation Directive ---------------------------------------------------> | + | Basic knowhow about media (speech) transmission with '''Session Description Protocol SDP''': |
| − | <!-- Transclusion : Article Begin -----------------------------------------------------------------><section begin=article />
| + | :* [[ {{NAMESPACE}}:support_voip_protocol#SupportSdpBasics | Basics about SDP Protocol ]] |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserIntroSupportLevel2 }} <!-------------------------------------------------------->
| + | <!-- Transclusion : Intro End --------------------------------------------------------------------><section end=intro /> |
| − | = Introduction Support Level 2 =
| |
| | | | |
| − | The level 2 support is the first instance where the user's telephony problems are handled that a user cannot solve himself. Additionally the level 2 supporter must be able to detect if the user problem is a "single" problem or if there is a large scale problem, that produces the same problem for multiple customers, e.g. data transfer problems in the Internet so that no VoIP call signaling is possible.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | __TOC__ <!-- Table of Contents --------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| | | | |
| − | The level 2 supporter must be aware of the complexity of a VoIP system and the multitude of telephony solutions on the user side. Further he needs an understanding of:
| |
| − | :* IP networking
| |
| − | :* [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_voip_protocol | VoIP protocols ]] SIP for signaling, SDP and RTP for speech transmission.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | <!-- Transclusion : Article Begin -----------------------------------------------------------------><section begin=article /> |
| | + | {{ToTop | SupportSipKnowhow }} <!------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| | + | = Knowhow Connection Signaling with "Session Initiation Protocol SIP" = |
| | | | |
| − | Overview of a VoIP system and the multitude of user telephony solutions:<br>
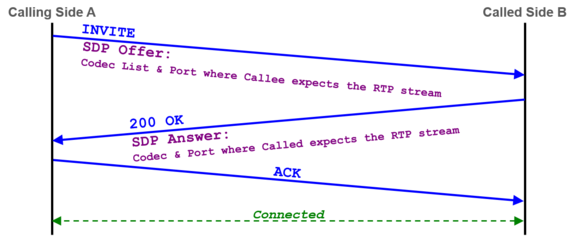
| + | The '''Session Initiation Protocol SIP''' is a communications protocol for signaling and controlling multimedia communication sessions. One of the most common applications of SIP is in Internet telephony for voice and video calls. |
| − | [[file:support_analyzing_3x3_equipment_setup_all_e.png |750px|frameless|left|link=| Overview of a VoIP system and the multitude of user telephony solutions]]
| |
| − | <br clear=all>
| |
| | | | |
| | + | For an extended overview of the SIP protocol visit: |
| | + | : <tt>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Session_Initiation_Protocol Wikipedia: Session Initiation Protocol SIP]</tt> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | The level 2 supporter faces problems with the following layers:
| |
| − | # Equipment
| |
| − | # IP data transfer
| |
| − | # Telephony service
| |
| | | | |
| − | And each of this layer can be located into the following raw areas:
| + | {{ToTop | SupportSipBasics }} <!-------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| − | # Customer/User site
| + | == Basics: Session Session Protocol SIP == |
| − | # Internet Service Provider ISP
| |
| − | # Telephony Provider
| |
| | | | |
| − | This layer and dividing into areas produces a "3x3 Support Matrix":<br>
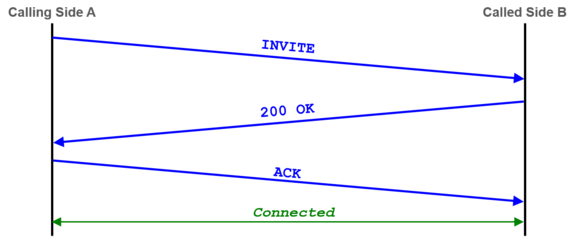
| + | Example of a "SIP dialog" with the minimal needed messages for a connection setup or connection renegotiation: |
| − | [[file:support_analyzing_3x3_matrix_notes_e.png |750px|frameless|left|link=| 3x3 Support Matrix with notes]] | + | [[file:support_sip_connection_setup.png |575px|left|frameless|link=| SIP Connection Establishing ]] |
| | <br clear=all> | | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | Within this "3x3 Support Matrix" the supporter can:
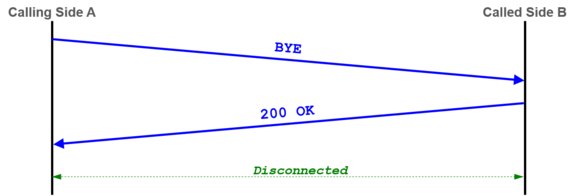
| + | Example of a "SIP dialog" with the minimal needed messages for a connection release: |
| − | :* advice the customer what to do when the problem is located in the nodes 1-T, 1-D and 1-E
| + | [[file:support_sip_connection_release.png |575px|left|frameless|link=| SIP Connection Release ]] |
| − | :* check the customer configurations on the VoIP Switch, node 3-T, and, if he has operator rights, adjust configurations.
| |
| − | | |
| − | For the other cases the level 2 supporter must be able to identify if:
| |
| − | :* the user must contact his ISP, due to possible Internet access problems
| |
| − | :* the VoIP System administrator must be involved, due to possible telephony service problems
| |
| − | : Hint:
| |
| − | : These cases indicate mostly large scale problems within the VoIP system!
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemIdentifyingBestPractice }} <!------------------------------------------>
| |
| − | = Best Practice for Handling an User Problem =
| |
| − | | |
| − | {{Note | type=bestpractice |
| |
| − | # Record the customer's data and problem description:
| |
| − | #* Get the customer data
| |
| − | #* Get the problem description from the customer
| |
| − | #: {{Picture_Help_Link | size=25 }} [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_user_level2#SupportUserProblemIdentifying | Show me how ... ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Cross check the user input against the VoIP switch configuration and logs.
| |
| − | #: Via ConfigCenter check the users account configuration:
| |
| − | #:* Telephone number registration
| |
| − | #:* TopStop
| |
| − | #:* RuleSet
| |
| − | #:* Consult the "Call Data" for the last connection attempts and connections longer than 2min
| |
| − | #: {{Picture_Help_Link | size=25 }} [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_user_level2#SupportUserProblemCheckUserInput | Show me how ... ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Evaluate the user's VoIP setup:
| |
| − | #* For questioning and analyzing the user's problem it is necessary that the supporter is aware of the VoIP setup of the user.
| |
| − | #: {{Picture_Help_Link | size=25 }} [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_user_level2#SupportUserProblemAnalyzing | Show me how ... ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Check the big picture:
| |
| − | #* If you are sure that the problem is "single" one continue with the next step "Solve the customer problem"
| |
| − | #* If you suspect that the customer is not the only one with this problem within a short time range, e.g. 30min, then contact the VoIP switch administrator/operator if there is known issue in the VoIP system that causes this type of problem.
| |
| − | #: {{Picture_Help_Link | size=25 }} [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_user_level2#SupportUserProblemBigPicture | Show me how ... ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Solve the customer's problem:
| |
| − | #* You have now enough basic information for solving the customer's problem
| |
| − | #: {{Picture_Help_Link | size=25 }} [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_user_level2#SupportUserProblemSolve | Show me how ... ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # If you are not able to solve this problem then contact the provider support. Have ready all collected information and what you have done and found out until now.
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The supporter shall record the user information and the results of the own research:
| |
| − | [[file:support_user_problem_analyzing_e.png |750px|frameless|left|link=| Identifying the User Problem ]] | |
| | <br clear=all> | | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ Note |
| |
| − | This information is most welcome if the supporter needs the support of the provider and has to inform him about the case.
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemIdentifying }} <!------------------------------------------------------>
| |
| − | = Step 1: Record the Customer's Data and Problem Description =
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop }} <!-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | == Get the Customer's Data ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | From the customer get:
| |
| − | :* Name of the caller
| |
| − | :* Telephone number of the caller
| |
| − | :* if applicable the company name
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop }} <!-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | == Write down the Customer's Problem Description ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | From the customer get:
| |
| − | :* Date and time of the issue
| |
| − | :* The involved telephone numbers
| |
| − | :* The problem description
| |
| − |
| |
| − | If the customer doesn't know then identify via the ConfigCenter the telephone number and its associated account.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemCheckUserInput }} <!-------------------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | = Step 2: Cross Check the User Inputs =
| |
| − |
| |
| − | With this cross check the supporter can validate the user information, gets an impression of the state of the account and will probably find the reason for the user problem...
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Via ConfigCenter check the users status and account configuration on the VoIP Switch:
| |
| − | # Check "Validity":
| |
| − | #: Check if the user account and its addresses are existing and "valid".
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Check [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_tools#SupportToolConfigCenterRegistration | the telephone number registration status. ]]
| |
| − | #: If there is no registration you can proceed directly with {{Picture_Help_Link | size=25 }} [[#SupportUserProblemDeviceNetwork | The user device is not registered ... ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Check "TopStop":
| |
| − | #: Check if a TopStop in the account or address prevents the user from doing outgoing calls.
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Check "RuleSet":
| |
| − | #: Check if a RuleSet in the account or address prevents the user from doing outgoing or receiving calls.
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Check "Call Forwards" or "Call Rejecting":
| |
| − | #: Check if a "Call Forwards" or "Call Rejecting" in the account prevents the user from doing outgoing or receiving calls.
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Check "Call Data":
| |
| − | #: Consult the [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_tools#SupportToolConfigCenterCallData | "Call Data" ]] for the last connection attempts and connections longer than 2min of the user.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemAnalyzingVoipSetup }} <!----------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | = Step 3: Evaluate the User's VoIP Setup =
| |
| − |
| |
| − | For questioning and analyzing the user's problem it is necessary that the supporter is aware of the VoIP setup of the user.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The experienced supporter knows of the user's VoIP setup after the [[#SupportUserProblemCheckUserInput | cross check ]]. If not here the supporter finds the most implemented VoIP setup's.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemAnalyzingVoipSetupResidential }} <!------------------------------------>
| |
| − | == VoIP Setup: Residential ==
| |
| − | Characteristics:<br>
| |
| − | :* Private household
| |
| − | :* Single or few telephone number
| |
| − | :* Each telephone number registers individually
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | Most common problems:<br>
| |
| − | :* Account or telephone number blocked on the VoIP switch
| |
| − | :* Telephone number not correctly ported to the telephony provider
| |
| − | :* Telephone not correctly configured
| |
| − | :* Telephone, cables defect
| |
| − | :* Internet access fails
| |
| | | | |
| | + | {{ToTop | SupportSipFlow }} <!---------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| | + | == Examples: SIP Signaling Flows == |
| | | | |
| − | Overview VoIP Setup:<br>
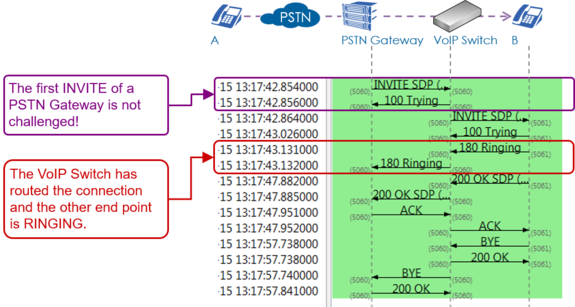
| + | Example of a regular outgoing call into the PSTN: |
| − | [[file:support_analyzing_voip_setup_scenario_residential_e.png |750px|frameless|left|link=| Overview VoIP Setup "Residential" ]] | + | [[file:support_sip_flow_pstn_outgoing_regular.png |680px|left|frameless|link=| SIP Flow PSTN Outgoing ]] |
| | <br clear=all> | | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | | + | Example of a regular incoming call from the PSTN: |
| − | | + | [[file:support_sip_flow_pstn_incoming_regular.png |575px|left|frameless|link=| SIP Flow PSTN Incoming ]] |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemAnalyzingVoipSetupIsdnLegacyPbx }} <!---------------------------------->
| |
| − | == VoIP Setup: Legacy ISDN PBX ==
| |
| − | Characteristics:<br>
| |
| − | :* Company PBX
| |
| − | :* The ISDN PBX is connected via BRI or PRI to an ISDN-SIP Gateway
| |
| − | :* One or more telephone number ranges
| |
| − | :* The telephone numbers are registered via a main number
| |
| − | :* The telephone number of incoming calls are signaled with only a few digits
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Most common problems:<br>
| |
| − | :* Account or telephone numbers blocked on the VoIP switch
| |
| − | :* Telephone number ranges not correctly ported to the telephony provider
| |
| − | :* Wrong incoming telephone number signaling
| |
| − | :* Internet access fails
| |
| − | :* The company Firewall VoIP ALG interferes with the SIP signaling or needed IP ports are blocked.
| |
| − | :* QoS problems for speech, Fax, DECT | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Overview VoIP Setup:<br>
| |
| − | [[file:support_analyzing_voip_setup_scenario_business_legacy_pbx_e.png |750px|frameless|left|link=| Overview VoIP Setup "Legacy ISDN PBX" ]] | |
| | <br clear=all> | | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
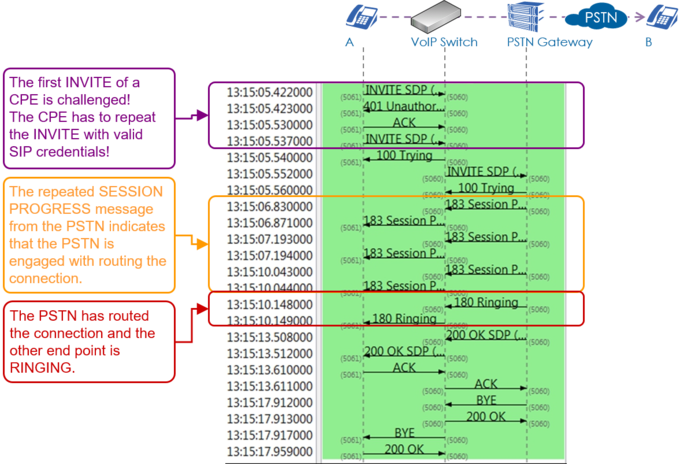
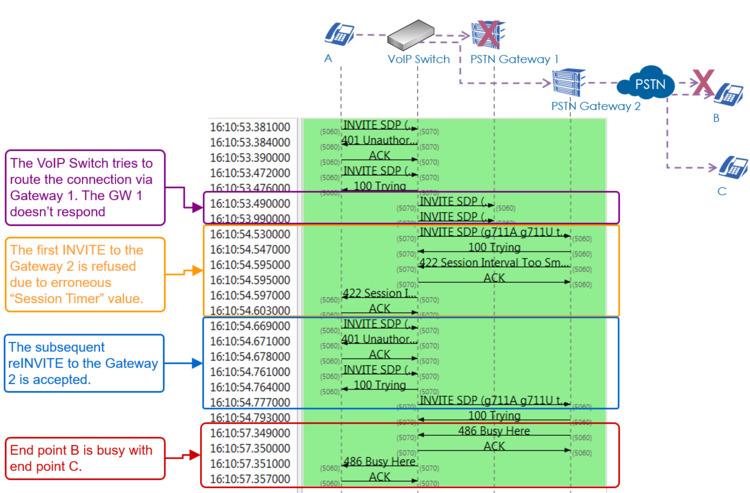
| − | | + | Example of an outgoing call into the PSTN with three exceptional signaling situations: |
| − | | + | :# The PSTN Gateway 1 doesn't respond so the VoIP Switch has to re-route to the PSTN Gateway 2 |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemAnalyzingVoipSetupIpPbx }} <!------------------------------------------>
| + | :# The telephone on side A offers an invalid "Session Time" value which is refused by the PSTN Gateway 2. The telephone on side A has to do a reINVITE with an acceptable "Session Time" value. |
| − | == VoIP Setup: IP PBX ==
| + | :# End point B is busy. |
| − | Characteristics:<br>
| + | [[file:support_sip_flow_pstn_outgoing_gw_failover_regular.png |750px|left|frameless|link=| SIP Flow GW Fail Over ]] |
| − | :* Company PBX
| |
| − | :* The IP PBX is connected directly or via SBC to the VoIP Switch
| |
| − | :* One or more telephone number ranges | |
| − | :* The telephone numbers are registered via a main number
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Most common problems:<br>
| |
| − | :* Account or telephone numbers blocked on the VoIP switch
| |
| − | :* Telephone number ranges not correctly ported to the telephony provider
| |
| − | :* The company Firewall and/or SBC VoIP ALG interferes with the SIP signaling or needed IP ports are blocked.
| |
| − | :* Internet access fails | |
| − | :* QoS problems for speech
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Overview VoIP Setup:<br>
| |
| − | [[file:support_analyzing_voip_setup_scenario_business_ip_pbx_e.png |750px|frameless|left|link=| Overview VoIP Setup "IP PBX" ]] | |
| | <br clear=all> | | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
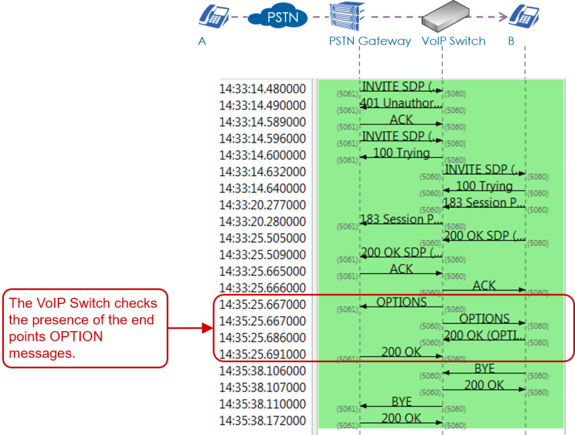
| − | | + | Example of a connection where the VoIP Switch checks the presence of the end points with OPTION messages. The VoIP Switch would release the connection if one end point doesn't respond with "200 OK": |
| − | | + | [[file:support_sip_flow_pstn_outgoing_options_regular.png |575px|left|frameless|link=| SIP Flow PSTN Outgoing Options ]] |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemAnalyzingVoipSetupIsdnVPbx }} <!---------------------------------->
| |
| − | == VoIP Setup: vPBX ==
| |
| − | Characteristics:<br>
| |
| − | :* Company PBX
| |
| − | :* The IP Phones are connected directly to the VoIP Switch
| |
| − | :* One or more telephone number ranges
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Most common problems:<br>
| |
| − | :* Public account and/or public telephone numbers blocked on the VoIP switch
| |
| − | :* Public telephone number ranges not correctly ported to the telephony provider
| |
| − | :* Private account and/or private telephone numbers blocked on the VoIP switch
| |
| − | :* Provisioning of the SIP devices out of the AdminCenter
| |
| − | :* The company or home office Firewalls and/or SBCs VoIP policies or ALG interferes with the SIP signaling or needed IP ports are blocked.
| |
| − | :* Company/home office Internet access fails
| |
| − | :* QoS problems for speech, FAX, DECT
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Overview VoIP Setup:<br>
| |
| − | [[file:support_analyzing_voip_setup_scenario_vpbx_e.png |750px|frameless|left|link=| Overview VoIP Setup "vPBX" ]] | |
| | <br clear=all> | | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| Line 272: |
Line 77: |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemBigPicture }} <!--------------------------------------------------------> | + | {{ToTop | SupportSipResponseCodes }} <!------------------------------------------------------------> |
| − | = Step 4: Check the Big Picture =
| + | == SIP Response Codes == |
| − | | |
| − | At this point the supporter should get aware if the problem is limited to this user or if it could be large scale problem within the VoIP System.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If the supporter suspects a large scale problem, due to a great amount of the same ore similar user complains then he should contact the telephony provider support or emergency organization.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | If the supporter has enough privileges he can check:
| |
| − | # The [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_tools#SupportToolConfigCenterComponent | VoIP Switch component status ]]
| |
| − | #: This will show if the VoIP Switch itself has a problem.
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # The [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_monitor | VoIP System monitor ]]
| |
| − | #: Here you can check if:
| |
| − | #:* The registrations dropped in a large scale
| |
| − | #:* The calls dropped in a large scale
| |
| − | #:* The IP connectivity somewhere in the VoIP system failed
| |
| − | | |
| − | At any rate the supporter '''must inform''' the VoIP system administrator!
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | <!-- PAGE BREAK --> <!-- PDF Creation Directive --------------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemSolve }} <!------------------------------------------------------------>
| |
| − | = Step 5: Solve the Customer Problem = | |
| | | | |
| | + | A list of SIP response codes and their meaning can be found here: |
| | + | :<tt>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_SIP_response_codes Wikipedia: List of SIP Response Codes ]</tt> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemDeviceNetwork }} <!---------------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | == Solve "Device / Network / Configuration / Registration" Problems ==
| |
| | | | |
| − | This problem type covers the following erroneous conditions:
| + | {{ToTop}} <!---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| − | :* The device doesn't start
| + | === Most Important 1xx—Provisional Responses === |
| − | :* The device doesn't integrate into the IP network
| |
| − | :* The device is not correctly configured
| |
| − | :* The device doesn't register at the VoIP Switch
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''100 Trying'''<br> |
| | + | Extended search being performed may take a significant time so a forking proxy must send a 100 Trying response. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Note |
| + | '''180 Ringing'''<br> |
| − | If the device is connected to an IP-PBX then these problems must be solved with the responsible of the IP-PBX.
| + | Destination user agent received INVITE, and is alerting user of call. |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''183 Session in Progress'''<br> |
| | + | This response may be used to send extra information for a call which is still being set up. |
| | | | |
| | + | <!-- |
| | + | '''181 Call is Being Forwarded'''<br> |
| | + | Servers can optionally send this response to indicate a call is being forwarded. |
| | | | |
| | + | '''182 Queued'''<br> |
| | + | Indicates that the destination was temporarily unavailable, so the server has queued the call until the destination is available. A server may send multiple 182 responses to update progress of the queue. |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemDeviceNetworkDeviceHwSw }} <!------------------------------------------>
| + | '''199 Early Dialog Terminated'''<br> |
| − | === Solve "Device Hardware & Firmware" Problem ===
| + | Can be used by User Agent Server to indicate to upstream SIP entities (including the User Agent Client (UAC)) that an early dialog has been terminated. |
| | + | --> |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 1 | Is the device powered on, not defect? }}
| |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | e1=
| |
| − | Check if the device correctly powered and shows basic activity?
| |
| − | :* Is the power cable correctly plugged in?
| |
| − | :* Is the power cable not defect?
| |
| − | :* Does the device show power on indication, e.g. display on, LED on?
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Replace the power cable
| |
| − | :: → Replace defect device if the powering is ok but no working indication is displayed
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Note| type=warning |
| |
| − | Defect power cables must be replaced!<br>
| |
| − | Faulty power cables can be life-threatening!
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | {{ToTop}} <!---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| | + | === Most Important 2xx—Successful Responses === |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 2 | Is the device connected to the IP network? }}
| + | '''200 OK'''<br> |
| | + | Indicates the request was successful. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| + | <!-- |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| + | '''202 Accepted'''<br> |
| − | | e1=
| + | Indicates that the request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. |
| − | Is the device correctly connected to the IP network?
| |
| − | :* Is the patch cable correctly plugged in?
| |
| − | :* Is the patch cable not defect?
| |
| − | :* Are there LED flashing or glow next to the network plug on the device or at the peer device (access router, IP switch)?
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Replace the patch cable
| |
| − | :: → Plug in the patch cable at a different port at the peer device (access router, IP switch)
| |
| − | :: → Replace defect device if the patch cable and peer port is ok but no working indication is displayed at the device port.
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''204 No Notification'''<br> |
| | + | Indicates the request was successful, but the corresponding response will not be received. |
| | + | --> |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 3 | Has the device a reasonable firmware loaded? }}
| |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | e1=
| |
| − | Has the device a reasonable firmware loaded?
| |
| − | :* The user must check the loaded firmware
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Replace the firmware if outdated or important bugs are fixed
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | {{ToTop}} <!---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| | + | === Most Important 3xx—Redirection Responses === |
| | | | |
| | + | '''302 Moved Temporarily'''<br> |
| | + | The client should try at the address in the Contact field. If an Expires field is present, the client may cache the result for that period of time. |
| | | | |
| | + | <!-- |
| | + | '''300 Multiple Choices'''<br> |
| | + | The address resolved to one of several options for the user or client to choose between, which are listed in the message body or the message's Contact fields. |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemDeviceNetworkDeviceIp }} <!-------------------------------------------->
| + | '''301 Moved Permanently'''<br> |
| − | === Solve "Device Network" Problem ===
| + | The original Request-URI is no longer valid, the new address is given in the Contact header field, and the client should update any records of the original Request-URI with the new value. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 1 | Has the device an IP address and can access the Internet? }}
| + | '''305 Use Proxy'''<br> |
| | + | The Contact field details a proxy that must be used to access the requested destination. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| + | '''380 Alternative Service'''<br> |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| + | The call failed, but alternatives are detailed in the message body. |
| − | | d1=
| + | --> |
| − | Has the device got an IP address?
| |
| − | :* Check on the device if it has received an IP address, e.g. via display or maintenance GUI.
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :* If no IP address was assigned the user must:
| |
| − | :* → Check if the device is really connected to the IP network!
| |
| − | :* → Check if the device is configured with a fixed IP address!
| |
| − | :*: If it has a fixed IP does it match with the IP subnet?
| |
| − | :*: Is the default GW and DNS entry configured?
| |
| − | :* → Check if the device is configured to use DHCP!
| |
| − | :*: if the DHCP service in the IP network is running
| |
| − | :*: If the user cannot check the DHCP service he must contact the company IT responsible or the responsible of maintaining the access router.
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | Has the device access toward the VoIp Switch?
| |
| − | :* Check if the device makes contact with the VoIP Switch via Internet or any private IP Link.
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :* → If the device shall connect via the Internet:
| |
| − | :*: Connect a PC to the Ethernet port where the device usually is connected and try to connect to any public Web site.
| |
| − | :* → If the device shall connect via an private network check with the IT responsible if the access to the VoIP Switch is guaranteed.
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | {{ToTop}} <!---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| | + | === Most Important 4xx—Client Failure Responses === |
| | | | |
| | + | '''400 Bad Request'''<br> |
| | + | The request could not be understood due to malformed syntax. |
| | | | |
| | + | '''401 Unauthorized'''<br> |
| | + | The request requires user authentication. This response is issued by UASs and registrars. |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemDeviceNetworkRegistration }} <!---------------------------------------->
| + | '''403 Forbidden'''<br> |
| − | === Solve "Registration" Problem ===
| + | The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfil it. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 1 | Review the account and telephone number configuration }}
| + | '''404 Not Found'''<br> |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| + | The server has definitive information that the user does not exist at the domain specified in the Request-URI. This status is also returned if the domain in the Request-URI does not match any of the domains handled by the recipient of the request. |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | t3=
| |
| − | Check via ConfigCenter:
| |
| − | :* Does the user account exist and is it "valid"?
| |
| − | :* Does the telephone number exist and is it "valid"?
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :* → Check why the account, telephone number doesn't exist or is disabled
| |
| − | :*: → activate them if allowed.
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''406 Not Acceptable'''<br> |
| | + | The resource identified by the request is only capable of generating response entities that have content characteristics but not acceptable according to the Accept header field sent in the request. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 2 | Where REGISTER messages received from the device on the VoIP Switch? }}
| + | '''408 Request Timeout'''<br> |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| + | Couldn't find the user in time. The server could not produce a response within a suitable amount of time, for example, if it could not determine the location of the user in time. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time. |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | t3=
| |
| − | In the [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_tools#SupportToolConfigCenterSupportLog | "Support Log" ]] search for the device registration in the present and past time.
| |
| − | # Set the "Support Log" filters
| |
| − | #:* Insert at "Text" the account name
| |
| − | #:* Insert at "From" - "Until" a reasonable time span where registrations could be expected
| |
| − | #:* Select the category: "Registration"
| |
| − | # Start the search and find out according the results what is going wrong.
| |
| − | # If needed repeat the search with the telephone number in the "Text" or other time spans
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | :* Check the log results {{Picture_Help_Link | size=25 }} see below
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :* {{Picture_Help_Link | size=25 }} see below
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''410 Gone'''<br> |
| | + | The user existed once, but is not available here any more. |
| | | | |
| − | Failed registrations due to disabled account or address:<br>
| + | '''480 Temporarily Unavailable'''<br> |
| − | {{ SW_Code ||
| + | Callee currently unavailable. |
| − | 2017-09-15-07:56:49.553 Registration failed, disabled account aan1-00093 tried to register number 0449980010
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :* Check why the account is disabled and activate if allowed.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''486 Busy Here'''<br> |
| | + | Callee is busy. |
| | | | |
| − | Failed registrations due to wrong SIP credentials:<br>
| + | '''487 Request Terminated'''<br> |
| − | {{ SW_Code ||
| + | Request has terminated by bye or cancel. |
| − | 2017-09-15-08:05:38.117 Registration failed, invalid credentials for account acc-01 <br>
| |
| − | 2017-09-15-08:05:39.112 Registration failed, unknown username 'myusername' tried to register '0123456789' <br>
| |
| − | 2017-09-15-08:05:38.377 Registration failed, unknown number '0987654321' tried to register for account acc-01 <br>
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :* The user must manually adjust the SIP credentials on the device
| |
| − | :* The user must re-configure the device via AdminCenter
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''488 Not Acceptable Here'''<br> |
| | + | Some aspect of the session description or the Request-URI is not acceptable. |
| | | | |
| − | The device didn't refresh its registration:<br>
| + | <!-- |
| − | {{ SW_Code ||
| + | '''402 Payment Required'''<br> |
| − | 2017-09-15-07:59:00.862 RegID989961 ended for 0987654321 ip=111.111.111.111:65398 ua=my-device v1.0
| + | Reserved for future use. |
| − | }}
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :* Order the user to check if the device is really on-line!
| |
| − | :* Order the user to check if the device is defect? powered on? patch? IP address? → see below
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''405 Method Not Allowed'''<br> |
| | + | The method specified in the Request-Line is understood, but not allowed for the address identified by the Request-URI.[1]: |
| | | | |
| − | For information a successful registration:<br>
| + | '''407 Proxy Authentication Required'''<br> |
| − | {{ SW_Code ||
| + | The request requires user authentication. This response is issued by proxys. |
| − | 2017-09-15-07:59:30.383 RegID989965 started for 0987654321 ip=111.111.111.111:65398 ua=my-device v1.0
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''409 Conflict'''<br> |
| | + | User already registered. |
| | | | |
| − | Hint:<br>
| + | '''411 Length Required'''<br> |
| − | The supporter might try to find REGISTER messages from the device in the [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_tools#SupportToolConfigCenterTrace | "Trace" ]]. This gives the certainty that the message was received by the VoIP switch. The supporter can filter for the telephone number. | + | The server will not accept the request without a valid Content-Length. |
| − | If the IP address is needed then the customer must be able to tell or evaluate it, e.g.:
| |
| − | : <tt>https://www.whatismyip.com/</tt>
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''412 Conditional Request Failed'''<br> |
| | + | The given precondition has not been met. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 3 | Is the device correctly configured for registration?? }}
| + | '''413 Request Entity Too Large'''<br> |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| + | Request body too large. |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | t1=
| |
| − | For a manually configured device, check that the device has the correct configuration for:
| |
| − | :* Telephone number
| |
| − | :* SIP credentials
| |
| − | :* VoIP Switch domain configuration
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → The user must manually check the device configuration and if needed adjust its configuration of the telephone number, SIP credentials and VoIP Switch domain for registration
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''414 Request-URI Too Long'''<br> |
| | + | The server is refusing to service the request because the Request-URI is longer than the server is willing to interpret. |
| | | | |
| − | For a automatically via AdminCenter configured device check that:
| + | '''415 Unsupported Media Type'''<br> |
| − | :* the selected device type in the AdminCenter is identical to the physical one.
| + | Request body in a format not supported. |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → If not the same type then the user must re-configure the device via AdminCenter
| |
| | | | |
| − | For a automatically via AdminCenter configured device check that:
| + | '''416 Unsupported URI Scheme'''<br> |
| − | :* the user device has [[{{NAMESPACE}}:admincenter_subsc_phones#PageDiversionEntity | downloaded its configuration. ]]
| + | Request-URI is unknown to the server. |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → If the configuration is not downloaded then it must be checked if the device:
| |
| − | :::* has got an IP address in the local IP network
| |
| − | :::* has access to the Internet
| |
| − | :::* has access to the configuration download of the Telephony Provider.<br>
| |
| − | :::: By default this is the IP address of the VoIP Switch domain and uses the protocol HTTPS on TCP port 443. Check with the Telephone provider or via ConfigCenter > Menu "System" > "Zone Profiles"
| |
| − | :: → The user must check if the Firewall, SBC or Access Router doesn't block HTTPS traffic to and from the configuration download of the Telephony Provider
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''417 Unknown Resource-Priority'''<br> |
| | + | There was a resource-priority option tag, but no Resource-Priority header. |
| | | | |
| | + | '''420 Bad Extension'''<br> |
| | + | Bad SIP Protocol Extension used, not understood by the server. |
| | | | |
| | + | '''421 Extension Required'''<br> |
| | + | The server needs a specific extension not listed in the Supported header. |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemConnectionSignaling }} <!--------------------------------------------->
| + | '''422 Session Interval Too Small'''<br> |
| − | == Solve "Connection" Problems ==
| + | The received request contains a Session-Expires header field with a duration below the minimum timer. |
| | | | |
| − | This problem type covers the following erroneous conditions:
| + | '''423 Interval Too Brief'''<br> |
| − | :* Incoming or outgoing calls are not working
| + | Expiration time of the resource is too short. |
| − | :* Wrong called number
| |
| − | :* Call supervision
| |
| − | :* User device not registered
| |
| − | :* User device not correct configured
| |
| − | :* SIP signaling in general
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''424 Bad Location Information'''<br> |
| | + | The request's location content was malformed or otherwise unsatisfactory. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Note |
| + | '''428 Use Identity Header'''<br> |
| − | If the device is connected to an IP-PBX then these problems must be solved with the responsible of the IP-PBX.
| + | The server policy requires an Identity header, and one has not been provided. |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''429 Provide Referrer Identity'''<br> |
| | + | The server did not receive a valid Referred-By token on the request. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 1 | Review the account and telephone number configuration / registration? }}
| + | '''430 Flow Failed'''<br> |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| + | A specific flow to a user agent has failed, although other flows may succeed. This response is intended for use between proxy devices, and should not be seen by an endpoint (and if it is seen by one, should be treated as a 400 Bad Request response). |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | t3=
| |
| − | Do this check for the A and/or B telephone number if they are on-net numbers of the VoIP SWitch.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Check via ConfigCenter:
| + | '''433 Anonymity Disallowed'''<br> |
| − | :* Does the telephone number exist?
| + | The request has been rejected because it was anonymous. |
| − | :* Is the telephone number valid?
| |
| − | :* Is the user account valid?
| |
| − | :* Is the telephone number correctly registered
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Check why the account, telephone number doesn't exist or is disabled and activate if allowed.
| |
| − | :: → [[#SupportUserProblemDeviceNetwork | Check why the device is not registered ]] at the VoIP Switch
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''436 Bad Identity-Info'''<br> |
| | + | The request has an Identity-Info header, and the URI scheme in that header cannot be dereferenced. |
| | | | |
| − | Hint:<br>
| + | '''437 Unsupported Certificate'''<br> |
| − | :* If the device is not registered outgoing calls might be working but NO incoming call will work.
| + | The server was unable to validate a certificate for the domain that signed the request. |
| | | | |
| | + | '''438 Invalid Identity Header'''<br> |
| | + | The server obtained a valid certificate that the request claimed was used to sign the request, but was unable to verify that signature. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 2 | Was the called number correctly transmitted to the peer? }}
| + | '''439 First Hop Lacks Outbound Support'''<br> |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| + | The first outbound proxy the user is attempting to register through does not support the "outbound" feature of RFC 5626, although the registrar does. |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | t3=
| |
| − | Check via ConfigCenter:
| |
| − | # In the [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_tools#SupportToolConfigCenterCallData | "Call Data" ]] search for the erroneous call:
| |
| − | #* Set the "Call Data" filters:
| |
| − | #:* Insert at "Time" a reasonable time span where the erroneous call is to be expected.
| |
| − | #:* Set "Duration" to 00:00:00
| |
| − | #:* Insert at "Called Number" the called number
| |
| − | # Start the search and identify the CDR of the erroneous call in the list
| |
| − | #: If no CDR was found search for the "Calling Number"!
| |
| − | # Open the identified CDR and get the trace of the call, click the {{Dialog_Button | Trace }}
| |
| − | # Check if the called number in the "TO-Header" in all INVITE messages is correct:
| |
| − | #* Is the called number correct?
| |
| − | #*: Often the users don't dial all digits or wrong digits or the configured number on a direct call key is incorrect.
| |
| − | #* If the number is dialed correctly then it can be that the destination is not reachable.
| |
| − | #* Outgoing calls from a vPBX can miss the [[{{NAMESPACE}}:admincenter_pbx_account#FeaturevPbxPublicPrefix | public prefix ]]
| |
| − | # Check the peers call cancel reason:
| |
| − | #* [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_voip_protocol#SupportSipResponseCodes | SIP Failure Responses ]]
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Inform the user to dial the correct number.
| |
| − | :: → Try to reach the called number via an alternative telephone network, e.g. from a mobile telephone.
| |
| − | :: → Check with the support of the telephony provider why the called number is not reachable.
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''470 Consent Needed'''<br> |
| | + | The source of the request did not have the permission of the recipient to make such a request. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 3 | What is the reason of an interrupted connection? }}
| + | '''481 Call/Transaction Does Not Exist'''<br> |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| + | Server received a request that does not match any dialog or transaction. |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | t1=
| |
| − | Search in the [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_tools#SupportToolConfigCenterCallData | "Call Data" ]] for the erroneous call:
| |
| − | #* Set the "Call Data" filters:
| |
| − | #:* Insert at "Time" a reasonable time span where the erroneous call is to be expected.
| |
| − | #:* Set "Duration" to 00:00:00
| |
| − | #:* Insert at "Called Number" the called number
| |
| − | # Start the search and identify the CDR of the erroneous call in the list
| |
| − | #: → If no CDR was found search for the "Calling Number"!
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''482 Loop Detected.'''<br> |
| | + | Server has detected a loop. |
| | | | |
| − | Open the identified CDR and check for the release or reject reason:
| + | '''483 Too Many Hops'''<br> |
| − | :* Was the connection released by a peer, A or B side?
| + | Max-Forwards header has reached the value '0'. |
| − | :* Check cancel reason in "State" ([[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_voip_protocol#SupportSipResponseCodes | SIP Failure Responses ]])
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Inform the user about the release reason, e.g. his own device or the peer device released the call regularly (but probably nor expected).
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''484 Address Incomplete'''<br> |
| | + | Request-URI incomplete. |
| | | | |
| − | Check if a call was released due to call supervision:
| + | '''485 Ambiguous'''<br> |
| − | :* Variant 1: Session Timer was not refreshed:
| + | Request-URI is ambiguous. |
| − | :** Open the "Trace" of the connection and check if the connection was released due to missing RE-INVITE from the peers when the Session Timer run out.
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Inform the user that his device did not restart the Session Timer. The device configuration must be inspected an adjusted if needed.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''489 Bad Event'''<br> |
| | + | The server did not understand an event package specified in an Event header field. |
| | | | |
| − | :* Variant 2: SIP INFO were not answered by the peer:
| + | '''491 Request Pending'''<br> |
| − | :** Open the "Trace" of the connection and check if the connection was released due to not answered INFO messages that were sent from the VoIP Switch toward the peers. If activated the INFO's are sent usually every 120sec.
| + | Server has some pending request from the same dialog. |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Inform the user that his device did not answered INFO messages. It must be checke with the support of the device manufacturer if the device doesn't send 200 ACK when an empty INFO message was received ("SIP ping").
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''493 Undecipherable'''<br> |
| | + | Request contains an encrypted MIME body, which recipient can not decrypt.[1]:§21.4.28 |
| | | | |
| − | :* Variant 3: Missing RTP packets between the peers:
| + | '''494 Security Agreement Required'''<br> |
| − | :: This type of problem is a difficult one and hard to check and solve! [[#SupportUserProblemQos | It must be handled like a QoS problem. ]]
| + | The server has received a request that requires a negotiated security mechanism, and the response contains a list of suitable security mechanisms for the requester to choose between or a digest authentication challenge. |
| − | :: Media transferring devices as the MediaServer of the VoIP Switch, SBCs, SS7-Gateways, SIP-Trunks supervise the media stream of RTP packets. If after a certain time no RTP packets are transferred in a connection then such an instance can release the call. Typically after 30secs a connection is released if no RTP streams are detected.
| + | --> |
| − | :** [[{{ NAMESPACE}}:Support_voip_protocol#SupportRtpBasics | Open the "Media Trace" ]] of the connection and check if there are remarkable differences between the amount of sent and received or lost RTP packets.
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: {{Picture_Help_Link | size=25 }} [[#SupportUserProblemQos | See "Quality of Service QoS problem" below. ]]
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQos }} <!--------------------------------------------------------------> | + | {{ToTop}} <!---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| − | == Solve "Quality of Service QoS" Problems == | + | === Most Important 5xx—Server Failure Responses === |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | + | '''503 Service Unavailable'''<br> |
| | + | The server is undergoing maintenance or is temporarily overloaded and so cannot process the request. A "Retry-After" header field may specify when the client may reattempt its request. |
| | | | |
| | + | <!-- |
| | + | '''500 Server Internal Error'''<br> |
| | + | The server could not fulfill the request due to some unexpected condition. |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosIntroduction }} <!-------------------------------------------------->
| + | '''501 Not Implemented'''<br> |
| − | === Introduction ===
| + | The server does not have the ability to fulfill the request, such as because it does not recognize the request method. (Compare with 405 Method Not Allowed, where the server recognizes the method but does not allow or support it.) |
| | | | |
| − | This problem type covers the following erroneous conditions:
| + | '''502 Bad Gateway'''<br> |
| − | :* No voice transmission in one or both directions from the beginning of the connection
| + | The server is acting as a gateway or proxy, and received an invalid response from a downstream server while attempting to fulfill the request. |
| − | :* Bad voice quality during the connection due to crackle, interruptions, clicking, uow-ing
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''504 Server Time-out'''<br> |
| | + | The server attempted to access another server in attempting to process the request, and did not receive a prompt response. |
| | | | |
| − | "Quality of Service QoS" problems are nasty ones and often difficult to fix. The source of the problems is all too often somewhere in the data transmission "D Data Transfer" layer (but sometimes they are surprisingly simple):
| + | '''505 Version Not Supported'''<br> |
| − | :* The microphone or loadspeaker in the telephone handset defect
| + | The SIP protocol version in the request is not supported by the server. |
| − | :* Volume configuration in the telephone set wrong
| |
| − | :* Telephone defect
| |
| − | :* The company Intranet is not made ready for VoIP
| |
| − | :* Any device in the "D - Data Transfer" layer
| |
| | | | |
| | + | '''513 Message Too Large'''<br> |
| | + | The request message length is longer than the server can process. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Note |
| + | '''580 Precondition Failure'''<br> |
| − | Solving QoS-problems often requires the cooperation and active co-testing from the customer/user with the support personnel!<br>
| + | The server is unable or unwilling to meet some constraints specified in the offer. |
| − | It is paramount that the customer/user knows that QoS-problems are difficult to track down and to solve. And it is time consuming.
| + | --> |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | Naming of QoS-problem:<br>
| |
| − | : '''One/No-Way''':
| |
| − | :: There is no speech transmission in one or both directions from start of the connection:
| |
| − | ::* mostly due to no or blocked RTP data transmission
| |
| − | ::
| |
| − | : '''Glitch''':
| |
| − | :: There is speech transmission but it is disturbed:
| |
| − | ::* Crackle (small packet loss, jitter)
| |
| − | ::* Short interruption, clicking (bigger packet loss)
| |
| − | ::* Ouw-ing (jitter, transcoding)
| |
| − | ::* Echo (jitter)
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | + | {{ToTop}} <!---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| | + | === Most Important 6xx—Global Failure Responses === |
| | | | |
| | + | '''603 Decline'''<br> |
| | + | The destination does not wish to participate in the call, or cannot do so, and additionally the destination knows there are no alternative destinations (such as a voicemail server) willing to accept the call. |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosDisturbedDirection }} <!-------------------------------------------->
| + | <!-- |
| − | === 1st Step: Interview the User ===
| + | '''600 Busy Everywhere'''<br> |
| | + | All possible destinations are busy. Unlike the 486 response, this response indicates the destination knows there are no alternative destinations (such as a voicemail server) able to accept the call. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 1 | Interview the user carefully and identify the type of QoS-problem }}
| + | '''604 Does Not Exist Anywhere'''<br> |
| | + | The server has authoritative information that the requested user does not exist anywhere. |
| | | | |
| − | Get all information from the user:<br>
| + | '''606 Not Acceptable'''<br> |
| − | # Occurs the the QoS-problem with all peers or just with the given B peer?
| + | The user's agent was contacted successfully but some aspects of the session description such as the requested media, bandwidth, or addressing style were not acceptable. |
| − | #: Hint:
| + | --> |
| − | #: If the problem occurs only with the B peer then this is a strong indication that something is wrong on the B side!
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Is there no voice transmission, neither from <tt>A->B</tt> nor <tt>B->A</tt>?
| |
| − | #: → Type of QoS-problem: [[#SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeNoWay | "No-Way Connection" ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Is there voice transmission from <tt>A->B</tt> (B hears you) but none from <tt>B->A</tt> (you don't hear B)?
| |
| − | #: → Type of QoS-problem: [[#SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeOneWayAB | "One-Way Connection <tt>A->B</tt>" ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Is there voice transmission from <tt>B->A</tt> (you hear B) but none from <tt>A->B</tt> (B doesn't hear you)?
| |
| − | #: → Type of QoS-problem: [[#SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeOneWayBA | "One-Way Connection <tt>B->A</tt>"]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Are there during the connection crackle, interruptions, clicking, uow-ing in the voice transmission for both sides?
| |
| − | #: → Type of QoS-problem: [[#SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeGlitch | "Glitch Connection" ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Are there during the connection crackle, interruptions, clicking, uow-ing in the voice transmission from <tt>A->B</tt>?
| |
| − | #: → Type of QoS-problem: [[#SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeGlitchAB | "Glitch Connection <tt>A->B</tt>" ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Are there during the connection crackle, interruptions, clicking, uow-ing in the voice transmission from <tt>B->A</tt>?
| |
| − | #: → Type of QoS-problem: [[#SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeGlitchBA | "Glitch Connection <tt>B->A</tt>" ]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Uses the user an ISDN or DECT telephone behind an ISDN-PBX? Does the user have sharp clicking glitches in a regular or irregular interval? Do experience all users behind this ISDN-PBX this clicking?
| |
| − | #: Remember :
| |
| − | #: This points to a [[#SupportUserProblemQosIsdnPbx | synchronization problem of the ISDN-PBX!]]
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Is one peer A or B a mobile user?
| |
| − | #: Remember:
| |
| − | #: Mobile networks often have QoS-problems on the wireless links between the base station and the mobile device!
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | Action:
| |
| − | :: → Cross check the users information by checking the media transfer statistics of the affected connection, see "2 Step" below!
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosLocalize }} <!------------------------------------------------------> | + | {{ToTop | SupportSdpKnowhow }} <!------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| − | === 2nd Step: Localize the QoS-Problem === | + | = Knowhow Media Stream Signaling with "Session Description Protocol SDP" = |
| | | | |
| − | {{Note |
| + | The '''Session Description Protocol SDP''' describes how during a connection setup the end points negotiate the parameters of this exchange as session announcement, session invitation, and parameter. SDP does not deliver media itself but is used between end points for negotiation of media type, format, and all associated properties for voice, Fax, DTMF, bit transparent data etc.. |
| − | It is very important that the supporter is aware of of the localization of the problem. QoS-problems in the range of the "2 Internet Service Provider ISP" or "3 Telephony Provider" will affect usually a lot of users immediately.
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | For an extended overview of the SDP protocol visit [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Session_Initiation_Protocol Wikipedia]. |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 1 | Check the Big Picture }}
| |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_3x3 | + | {{Note| |
| − | |width1=290 | width2=290 | width3=295 <!--max 875--> | + | The VoIP Switch doesn't interfere in the SDP negotiation of the end points! |
| − | | d1=
| + | There may be exceptions for certain Customer Premises Equipment CPE devices where interoperation problems are known. Check with the VoIP switch administrator which CPE devices are known with SDP manipulations by the VoIP switch. |
| − | Check with the ISP where the user is connected to if there are outages in:
| |
| − | :* the ISP IP network
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Inform immediately the Telephone providers support or alarming organization.
| |
| − | :: → If yes, just wait until the outage is solved
| |
| − | | d2=
| |
| − | Check with the ISP where the VoIP System is connected to if there are outages in:
| |
| − | :* the ISP IP network
| |
| − | :* relevant national and/or international IP network
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Inform immediately the Telephone providers support or alarming organization.
| |
| − | :: → If yes, just wait until the outage is solved
| |
| − | | d3=
| |
| − | Check with the IT responsible of the IP network where the VoIP System is attached to: | |
| − | :* Are there known outages in the IP network where the VoIP System is attached to?
| |
| − | :* Is there a large scale QoS-problem?
| |
| − | :* Are users affected which are located:
| |
| − | ::* in a certain private IP network of the telephony provider?
| |
| − | ::* at a definable tenant?
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Inform immediately the Telephone providers support or alarming organization.
| |
| − | :: → If the VoIP System is located in a pure private IP network then contact immediately the IT responsible or IT emergency organization.
| |
| − | :: → If yes, just wait until the outage is solved
| |
| − | :
| |
| | }} | | }} |
| | | | |
| Line 767: |
Line 361: |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 2 | Identify the disturbed transmission direction from the VoIP Switch's view }} | + | {{ToTop | SupportSdpBasics }} <!-------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| | + | == Basics: Session Description Protocol SDP == |
| | | | |
| − | This identification bases upon the VoIP System setting that all media streams are routed via the MediaServer of the VoIP Switch. The MediaServer collects statistic information about all media stream that are routed through it. These statistics can help to identify the source of the QoS-problem.
| + | The SDP is embedded in the SIP messages during connection setup or connection renegotiation: |
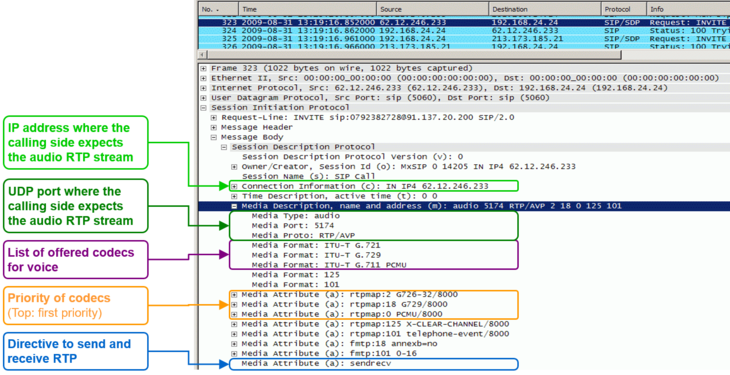
| | + | [[file:support_sip_connection_setup_with_sdp.png |575px|left|frameless|link=| SIP with SDP]] |
| | + | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | Search in the [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_tools#SupportToolConfigCenterCallData | "Call Data" ]] the CDR of the erroneous call:
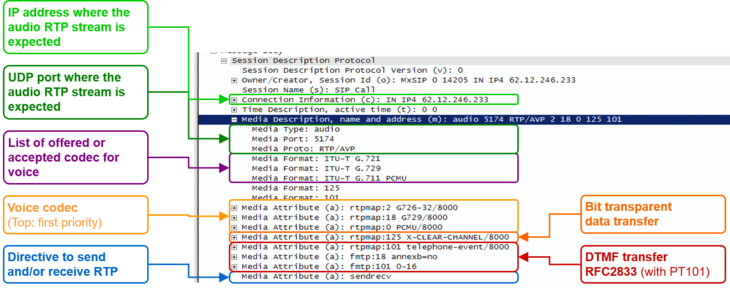
| + | The following SDP properties and parameters are important for supporting customer problems: |
| − | #* Set the "Call Data" filters:
| + | [[file:support_sdp_basic.png |730px|left|frameless|link=| SDP Basic Properties and Parameters ]] |
| − | #:* Insert at "Time" a reasonable time span where the erroneous call is to be expected.
| + | <br clear=all> |
| − | #:* Set "Duration" to 00:00:00
| |
| − | #:* Insert at "Called Number" the called number
| |
| − | # Start the search and identify the CDR of the erroneous call in the list
| |
| − | #: → If no CDR was found search for the "Calling Number"!
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Open the identified CDR
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | # Get the RTP statistics of this connection: click {{Dialog_Button | Media Trace }}
| |
| − | #: If there are no data in the "Media Trace" contained then the media stream is not routed via the MediaServer of the VoIP Switch. See below how to force the routing via the MediaServer.
| |
| − | #:
| |
| − | #: Depending of the identified QoS-problem type [[{{NAMESPACE}}:Support_voip_protocol#SupportRtpBasics | analyze the RTP statistics ]] detail, see below
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | If the media stream are not routed by default via MediaServer the supporter can force it for an account via the ConfigCenter:
| + | Example of a SDP offer from the calling side A: |
| − | {{Navigation_List | 1 | Menu "Account" }}
| + | [[file:support_sdp_offer.png |730px|left|frameless|link=| SDP Offer Calling Side A ]] |
| − | {{Navigation_List | 2 | Select the customers account }}
| + | <br clear=all> |
| − | {{Navigation_List | 3 | Tab "Advanced" }}
| |
| − | {{Navigation_List | 4 | Set "Use always MediaServer" to <tt>"Yes"</tt> }}
| |
| − | Note:
| |
| − | :* By forcing the media stream through the MediaServer the routing of the RTP packets through the IP networks changes!
| |
| − | :* If the QoS-problem disappears when forced via MediaServer and reappears when switched back then this is a strong indication that something is wrong in the direct IP routing path between the users and the peer device.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | <!-- |
| | + | Example of a SDP answer from the called side B: |
| | + | [[file:support_sdp_answer.png |730px|left|frameless|link=| SDP Answer Called Side B ]] |
| | + | <br clear=all> |
| | + | --> |
| | | | |
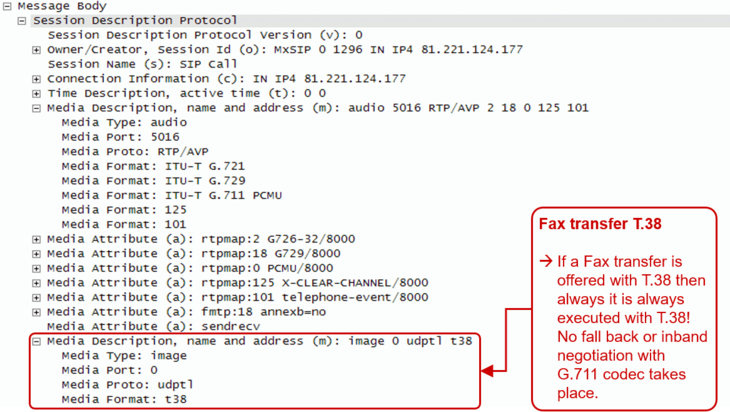
| | + | Example of a SDP offer for a Fax transfer with T.38 from the calling side A: |
| | + | [[file:support_sdp_t38.png |730px|left|frameless|link=| SDP Offer Calling Side A with T.38 ]] |
| | + | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeNoWay }} <!-------------------------------------------------> | + | Interpretation of the "Media Attributes": |
| − | ==== Localize "No-Way Connection" and Possible Actions ====
| + | {{Table_Start}} |
| − | | + | {{Table_Header | columns=4 | width1=50 | width2=150 | width3=250 | width4=550 |
| − | "No-Way Connection":<br>
| + | | header1= Index | header2= Type | header3= Attribute | header4= Remark }} |
| − | :* No voice transmission, neither from A->B nor B->A
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Knowhow background:<br>
| |
| − | :* May occur during commissioning of the customer connection for VoIP
| |
| − | :* May occur when the telephony provider introduce now IP networks for new telephony users
| |
| − | :* May occur when the Internet service provider or telephony provider modify the IP routing
| |
| − | :* Customer firewall policies block IP range or UDP port range
| |
| − | :* The peer devices negotiate not the same codec
| |
| − | :* May occur when IP devices are defect
| |
| − | :* User device defect
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | {{Support_3x3 | |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875--> | |
| − | | d3= | |
| − | Assumption:<br>
| |
| − | The problem reporting user/customer shall be the A leg.
| |
| − | | |
| − | <section begin=1stCodecCheck />
| |
| − | '''1st:''' Check if the negotiated "codec" are correct for both peers.
| |
| − | :* Check in the SDP information if the selected codec of the leg B side is in the offered list of leg A
| |
| − | ::* The B side codec must be within the codec list of side A
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: ouw-ing, No-Way or One-Way connection
| |
| − | | |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If the B side codec is not within the codec list of side A then check the configuration of the peer device B.
| |
| − | : → Check the configuration of the device A why the codec of side B is not in its list.
| |
| − | : → Consider a firmware upgrade of either device!
| |
| − | <section end=1stCodecCheck />
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | <section begin=1stIpAddressPortCheck />
| |
| − | '''2nd:''' Check if the negotiated IP address and UDP ports are not blocked by any firewall.
| |
| − | :* Check in the SDP information if the displayed IP addresses and UDP ports of the leg A and B are not blocked by any firewall
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: No-Way or One-Way connection
| |
| − | | |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → Adjust the customers firewall policies
| |
| − | : → Adjust the usable UDP port range in the customer peer device
| |
| − | <section end=1stIpAddressPortCheck />
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | '''3rd:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP transfer from and to the user/customer is not working:
| |
| − | :* Are there are no (or few) received packets from the user?
| |
| − | :* Are there packets sent toward the user?
| |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg A "rec"=0</tt> and <tt>Leg A "snt">0</tt>: no packets received from A but packets were sent toward A.
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If there is a gateway on the user/customer side which is provided from the Telephony provider then check the correct working of this gateway.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if the Internet or access to the Telephony network is ok.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if the access router or Firewall are ok (no blocking policies, VoIP ALG off, ...).
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if its IT infrastructure is ok (no faulty IP switches, routers, ...).
| |
| − | : → The user or customer PBX responsible must check if the ISDN- or IP-PBX is working correctly.
| |
| − | : → The user must check if the telephone device is ok.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | '''4th:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP transfer from and to the PSTN is not working:
| |
| − | :* Are there are no (or few) received packets from the PSTN? →
| |
| − | :* Are there packets sent toward the PSTN?
| |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg B "rec"=0</tt> and <tt>Leg B "snt">0</tt>: no packets received from B but packets were sent toward B
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → The supporter must inform immediately the telephony provider support or IT emergency organization.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | '''5th:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP handling in the VoIP Switch MediaServer is not working:
| |
| − | :* Are there are packets received from the PSTN but not sent toward the user?
| |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg B "rec">0</tt> and <tt>Leg A "snt"=0</tt>: packets from B received but no packets sent toward A
| |
| − | :* Are there are packets received from the user but not sent toward the PSTN?
| |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg A "rec">0</tt> and <tt>Leg B "snt"=0</tt>: packets from A received but no packets sent toward B
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → The supporter must inform immediately the telephony provider support!
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeOneWayAB }} <!---------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | ==== Localize "One-Way Connection <tt>A->B</tt> and Possible Actions ====
| |
| − | | |
| − | "One-Way Connection <tt>A->B</tt>":<br>
| |
| − | :* B hears A but A doesn't hear B
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Knowhow background:<br>
| |
| − | :* May occur during commissioning of the customer connection for VoIP
| |
| − | :* May occur when the telephony provider introduce now IP networks for new telephony users
| |
| − | :* May occur when the Internet service provider or telephony provider modify the IP routing
| |
| − | :* Customer firewall policies block IP range or UDP port range
| |
| − | :* The peer devices negotiate not the same codec
| |
| − | :* May occur when IP devices are defect
| |
| − | :* User device defect
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875--> | |
| − | | d3= | |
| − | Assumption:<br>
| |
| − | The problem reporting user/customer shall be the A leg.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | <section begin=1stCodecCheck />
| |
| − | '''1st:''' Check if the negotiated "codec" are correct for both peers.
| |
| − | :* Check in the SDP information if the selected codec of the leg B side is in the offered list of leg A
| |
| − | ::* The B side codec must be within the codec list of side A
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: ouw-ing, No-Way or One-Way connection
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If the B side codec is not within the codec list of side A then check the configuration of the peer device B.
| |
| − | : → Check the configuration of the device A why the codec of side B is not in its list.
| |
| − | : → Consider a firmware upgrade of either device!
| |
| − | <section end=1stCodecCheck />
| |
| | | | |
| | + | {{Table_Line | columns=4 | line=1 |
| | + | | col1= 0 | col2= PCMU | col3= ISDN G.711µlaw | col4= Very good quality VoIP codec }} |
| | | | |
| − | <section begin=1stIpAddressPortCheck />
| + | {{Table_Line | columns=4 | line=2 |
| − | '''2nd:''' Check if the negotiated IP address and UDP ports are not blocked by any firewall.
| + | | col1= 8 | col2= PCMA | col3= ISDN G.711alaw | col4= Very good quality VoIP codec }} |
| − | :* Check in the SDP information if the displayed IP addresses and UDP ports of the leg A and B are not blocked by any firewall
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: No-Way or One-Way connection
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → Adjust the customers firewall policies
| |
| − | : → Adjust the usable UDP port range in the customer peer device
| |
| − | <section end=1stIpAddressPortCheck />
| |
| | | | |
| | + | {{Table_Line | columns=4 | line=3 |
| | + | | col1= 2 | col2= G.726-32 | col3= | col4= Good quality VoIP codec }} |
| | | | |
| − | '''3rd:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP transfer from the PSTN is not working:
| + | {{Table_Line | columns=4 | line=4 |
| − | :* Are there are no (or few) received packets from the PSTN?
| + | | col1= 18 | col2= G.729 | col3= | col4= Low quality VoIP codec }} |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg B "rec"=0</tt>: no packets received from the PSTN.
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → The supporter must inform immediately the telephony provider support or IT emergency organization.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | {{Table_Line | columns=4 | line=5 |
| | + | | col1=125 | col2= x-clear-channel | col3= data service bit transparent | col4= Echo canceling will be switched off and the data bit by bit transferred }} |
| | | | |
| − | '''4th:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP transfer to the user/customer is working:
| + | {{Table_Line | columns=4 | line=6 |
| − | :* Are there are received packets from the PSTN and sent toward the user?
| + | | col1= 101 | col2= telephone-event | col3= DTMF, RFC 2833 | col4= DTMF will not be transferred inband but as RTP event according RFC 2833 }} |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg B "rec">0</tt> and <tt>Leg A "snt">0</tt>: packets were received from the PSTN and sent toward the user.
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If there is a gateway on the user/customer side which is provided from the Telephony provider then check the correct working of this gateway.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if the Internet or access to the Telephony network is ok.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if the access router or Firewall are ok (no blocking policies, VoIP ALG off, ...).
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if its IT infrastructure is ok (no faulty IP switches, routers, ...).
| |
| − | : → The user or customer PBX responsible must check if the ISDN- or IP-PBX is working correctly.
| |
| − | : → The user must check if the telephone device is ok.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | {{Table_Line | columns=4 | line=7 |
| | + | | col1= 18 | col2= annexb=0 | col3= Special information for codec with index 18 | col4= Special directive for codec G.729 }} |
| | | | |
| − | '''5th:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP handling in the VoIP Switch MediaServer is not working:
| + | {{Table_Line | columns=4 | line=8 |
| − | :* Are there are packets received from the PSTN but not sent toward the user?
| + | | col1= 101 | col2= 0-16 | col3= Special information for for telephone-event with index 101 |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg B "rec">0</tt> and <tt>Leg A "snt"=0</tt>: packets were received from the PSTN but not sent toward the user | + | | col4= |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| + | 0-15 : DTMF character 0-9, *,#, A,B,C,D <br> |
| − | : → The supporter must inform immediately the telephony provider support! | + | 0-16 : DTMF character 0-9, *,#, A,B,C,D, Flash |
| | }} | | }} |
| | + | {{Table_End}} |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeOneWayBA }} <!----------------------------------------------> | + | {{ToTop | SupportRtpBasics }} <!-------------------------------------------------------------------> |
| − | ==== Localize "One-Way Connection <tt>B->A</tt> and Possible Actions ====
| |
| − | | |
| − | "One-Way Connection <tt>B->A</tt>":<br>
| |
| − | :* A hears B but B doesn't hear A
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Knowhow background:<br>
| |
| − | :* May occur during commissioning of the customer connection for VoIP
| |
| − | :* May occur when the telephony provider introduce now IP networks for new telephony users
| |
| − | :* May occur when the Internet service provider or telephony provider modify the IP routing
| |
| − | :* Customer firewall policies block IP range or UDP port range
| |
| − | :* The peer devices negotiate not the same codec
| |
| − | :* May occur when IP devices are defect
| |
| − | :* User device defect
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | d3=
| |
| − | Assumption:<br>
| |
| − | The problem reporting user/customer shall be the A leg.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | <section begin=1stCodecCheck />
| |
| − | '''1st:''' Check if the negotiated "codec" are correct for both peers.
| |
| − | :* Check in the SDP information if the selected codec of the leg B side is in the offered list of leg A
| |
| − | ::* The B side codec must be within the codec list of side A
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: ouw-ing, No-Way or One-Way connection
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If the B side codec is not within the codec list of side A then check the configuration of the peer device B.
| |
| − | : → Check the configuration of the device A why the codec of side B is not in its list.
| |
| − | : → Consider a firmware upgrade of either device!
| |
| − | <section end=1stCodecCheck />
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | <section begin=1stIpAddressPortCheck />
| |
| − | '''2nd:''' Check if the negotiated IP address and UDP ports are not blocked by any firewall.
| |
| − | :* Check in the SDP information if the displayed IP addresses and UDP ports of the leg A and B are not blocked by any firewall
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: No-Way or One-Way connection
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → Adjust the customers firewall policies
| |
| − | : → Adjust the usable UDP port range in the customer peer device
| |
| − | <section end=1stIpAddressPortCheck />
| |
| − | | |
| | | | |
| − | '''3rd:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP transfer from the user is not working:
| + | == Basics: RTP/RTCP == |
| − | :* Are there are no (or few) received packets from the user?
| |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg A "rec"=0</tt>: no packets received from the user
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If there is a gateway on the user/customer side which is provided from the Telephony provider then check the correct working of this gateway.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if the Internet or access to the Telephony network is ok.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if the access router or Firewall are ok (no blocking policies, VoIP ALG off, ...).
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if its IT infrastructure is ok (no faulty IP switches, routers, ...).
| |
| − | : → The user or customer PBX responsible must check if the ISDN- or IP-PBX is working correctly.
| |
| − | : → The user must check if the telephone device is ok.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | The Real Time Protocol RTP is used to transfer media data, e.g. speech in VoIP based telephony. |
| | | | |
| − | '''4th:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP transfer to the PSTN is not working:
| + | The Real Time Control Protocol RTPC transfers periodically statistical media data between the peers of a connection. |
| − | :* Are there packets sent toward the PSTN?
| |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg A "rec">0</tt> and <tt>Leg B "snt">0</tt>: packets were received from the user but not sent toward the PSTN
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → The supporter must inform immediately the telephony provider support or IT emergency organization.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | If RTP packets are lost, delayed or jitter then we speak of a Quality of Service QoS problem. For the support it is of interest to know if the number of transferred packets between the peers of a connection and if the numbers in the receive and send paths are reasonable equal, if packets were lost on call leg etc. With these statistical media information it can be possible to identify a path or transfer direction were QoS problems occure. |
| | | | |
| − | '''5th:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP handling in the VoIP Switch MediaServer is not working:
| + | {{Note| |
| − | :* Are there are packets received from the user but not sent toward the PSTN?
| + | The media stream must be proxied via the MediaServer of the VoIP Switch in order to compute statistical numbers of a connection. |
| − | :: → If <tt>Leg A "snt">0</tt> and <tt>Leg B "snt"=0</tt>,
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → The supporter must inform immediately the telephony provider support!
| |
| | }} | | }} |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | + | The Aarenet VoIP Switch supports RTP/RTCP statistic data collection of a connection. How they can be obtained is described in article "Manual of the Aarenet VoIP Switch Support Tools", [[{{NAMESPACE}}:support_tools#SupportToolConfigCenterCallData | chapter "The ConfigCenter Call Data" ]] |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeGlitch }} <!------------------------------------------------>
| + | Overview of "RTP/RTCP" information collection: |
| − | ==== Localize "Glitch Connection" and Possible Actions ====
| + | [[file:support_connection_rtp_rtcp_statistics_e.png |1000px|left|frameless| Dialog: "RTP/RTCP" ]] |
| | + | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| − | "Glitch Connection":<br>
| |
| − | :* The voice transmission from A->B and B->A is disturbed
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Knowhow background:<br>
| |
| − | :* May occur when the customers Intranet is not optimized for VoIP
| |
| − | :* The peer devices negotiate not the same codec
| |
| − | :* May occur when IP devices are defect
| |
| − | :* User device defect
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | d3=
| |
| − | Assumption:<br>
| |
| − | The problem reporting user/customer shall be the A leg.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''1st:''' Check if the negotiated "codec" are correct for both peers.
| |
| − | :* Check in the SDP information if the selected codec of the leg B side is in the offered list of leg A:
| |
| − | :: The B side codec must be within the codec list of side A
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: ouw-ing, No-Way or One-Way connection
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If the B side codec is not within the codec list of side A then check the configuration of the peer device B.
| |
| − | : → Check the configuration of the device A why the codec of side B is not in its list.
| |
| − | : → Consider a firmware upgrade of either device!
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''2nd:''' Check the <tt>"rtcp data"</tt> and <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records from and to the user/customer:
| |
| − | :* Check the <tt>"rtcp data"</tt> (statistical data delivered from the device):
| |
| − | :: <tt>"lost>0"</tt>: Device A claimed not to receive all packets
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruptions
| |
| − | :: <tt>"jitter>0"</tt>: Device A claimed to receive packets delayed or wavering (if the jitter values are different then wavering)
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruptions, echo, ouw-ing
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | :* Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> (statistical data from the VoIP Switch):
| |
| − | :: <tt>"rec"</tt> not equal <tt>"snt"</tt>: The numbers of received <tt>"rec"</tt> and sent <tt>"snt"</tt> must be more or less equal since the last report.
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruptions
| |
| − | :: <tt>"cpkl>0.1"</tt>: The cumulated packet loss <tt>"cpkl"</tt> should be smaller than <tt>"<0.1"</tt>.
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, bigger interruptions
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If there is a gateway on the user/customer side which is provided from the Telephony provider then check the correct working of this gateway.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if the Internet or access to the Telephony network is ok.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if its IT infrastructure is ok (no faulty IP switches, routers, ...).
| |
| − | : → The user or customer PBX responsible must check if IP-PBX is working correctly.
| |
| − | : → The user must check if the telephone device is ok.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''3rd:''' Check the <tt>"rtcp data"</tt> and <tt>"rtp data"</tt>records from and to the PSTN is not working:
| |
| − | :* Check the <tt>"rtcp data"</tt> (statistical data delivered from the device):
| |
| − | :: <tt>"lost>0"</tt>: Device B claimed not to receive all packets.
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruptions
| |
| − | :: <tt>"jitter>0"</tt>: Device B claimed to receive packets delayed or wavering (if the jitter values are different then wavering).
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruption, echo, ouw-ing
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | :* Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> (statistical data from the VoIP Switch):
| |
| − | :: <tt>"rec"</tt> not equal <tt>"snt"</tt>: The numbers of received <tt>"rec"</tt> and sent <tt>"snt"</tt> must be more or less equal since the last report
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruption
| |
| − | :: <tt>"cpkl>0.1"</tt>: The cumulated packet loss <tt>"cpkl"</tt> should be smaller than <tt>"<0.1"</tt>
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, bigger interruptions
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If there are '''no''' similar problems in the big picture then the problem lies presumably in the network of side B.
| |
| − | : → If there are '''similar''' problems in the big picture then the supporter must inform immediately the telephony provider support or IT emergency organization.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeGlitchAB }} <!---------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | ==== Localize "Glitch Connection <tt>A->B</tt>" and Possible Actions ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | "Glitch Connection <tt>A->B</tt>":<br>
| |
| − | :* The voice transmission from A->B is disturbed. B claims to hear A with bad quality.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Knowhow background:<br>
| |
| − | :* May occur when the customers Intranet is not optimized for VoIP
| |
| − | :* May occur when IP devices are defect
| |
| − | :* User device defect
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | d3=
| |
| − | Assumption:<br>
| |
| − | The problem reporting user/customer shall be the A leg.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''1st:''' Check if the negotiated "codec" are correct for both peers.
| |
| − | :* Check in the SDP information if the selected codec of the leg B side is in the offered list of leg A:
| |
| − | :: The B side codec must be within the codec list of side A
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: ouw-ing, No-Way or One-Way connection
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If the B side codec is not within the codec list of side A then check the configuration of the peer device B.
| |
| − | : → Check the configuration of the device A why the codec of side B is not in its list.
| |
| − | : → Consider a firmware upgrade of either device!
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''2nd:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP transfer to the PSTN is correctly working:
| |
| − | :* Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> (statistical data from the VoIP Switch) toward the PSTN:
| |
| − | :: <tt>Leg A "rec"</tt> not equal <tt>Leg B "snt"</tt>: The numbers of received <tt>"rec"</tt> and sent <tt>"snt"</tt> must be more or less equal since the last report.
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruptions
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If the received packets are very different to the sent ones then the supporter must inform immediately the telephony provider support or IT emergency organization.
| |
| − | : → If the received packets are quite equal to the sent ones then the problem must be on the B side
| |
| − |
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosLocalizeGlitchBA }} <!---------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | ==== Localize "Glitch Connection <tt>B->A</tt>" and Possible Actions ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | "Glitch Connection <tt>B->A</tt>":<br>
| |
| − | :* The voice transmission from B->A is disturbed. A claims to hear B with bad quality.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Knowhow background:<br>
| |
| − | :* May occur when the customers Intranet is not optimized for VoIP
| |
| − | :* May occur when IP devices are defect
| |
| − | :* User device defect
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=75 | width2=75 | width3=725 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | d3=
| |
| − | Assumption:<br>
| |
| − | The problem reporting user/customer shall be the A leg.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''1st:''' Check if the negotiated "codec" are correct for both peers.
| |
| − | :* Check in the SDP information if the selected codec of the leg B side is in the offered list of leg A:
| |
| − | :: The B side codec must be within the codec list of side A
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: ouw-ing, No-Way or One-Way connection
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If the B side codec is not within the codec list of side A then check the configuration of the peer device B.
| |
| − | : → Check the configuration of the device A why the codec of side B is not in its list.
| |
| − | : → Consider a firmware upgrade of either device!
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''2nd:''' Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> records if the RTP transfer to the user/customer is correctly working:
| |
| − | :* Check the <tt>"rtp data"</tt> (statistical data from the VoIP Switch) toward the user/customer:
| |
| − | :: <tt>Leg B "rec"</tt> not equal <tt>Leg A "snt"</tt>: The numbers of received <tt>"rec"</tt> and sent <tt>"snt"</tt> must be more or less equal since the last report.
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruptions
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If the received packets are very different to the sent ones then the supporter must inform immediately the telephony provider support or IT emergency organization.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''3rd:''' Check the <tt>"rtcp data"</tt> records from the user/customer:
| |
| − | :* Check the <tt>"rtcp data"</tt> (statistical data delivered from the device):
| |
| − | :: <tt>"lost>0"</tt>: Device A claimed not to receive all packets
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruptions
| |
| − | :: <tt>"jitter>0"</tt>: Device A claimed to receive packets delayed or wavering (if the jitter values are different then wavering)
| |
| − | ::: Possible problems: crackle, short interruptions, echo, ouw-ing
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | : Actions:<br>
| |
| − | : → If there is a gateway on the user/customer side which is provided from the Telephony provider then check the correct working of this gateway.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if the Internet or access to the Telephony network is ok.
| |
| − | : → The user or customer IT responsible must check if its IT infrastructure is ok (no faulty IP switches, routers, ...).
| |
| − | : → The user or customer PBX responsible must check if IP-PBX is working correctly.
| |
| − | : → The user must check if the telephone device is ok.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemQosIsdnPbx }} <!----------------------------------------->
| |
| − | === Solve "Voice Glitches with ISDN-PBX" Problem ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This problem type covers the following erroneous conditions:
| |
| − | :* Bad speech quality in an ISDN-PBX environment
| |
| − | :* Glitches in the voice transmission, it "clicks"
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ISDN-PBX environment usually provide an excellent voice quality. In an VoIP environment this excellent voice quality can be only maintained if the ISDN-PBX can synchronize with high precision clock source.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 1 | Check the ISDN reference clock }}
| |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | e1=
| |
| − | Checks:
| |
| − | :* Does the ISDN-PBX take its clock reference from a high precision clock?
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Make sure the ISDN-PBX takes its reference clock from a high precision source.
| |
| − | :: → Use an ISDN-Gateway which provides a high precision clock.
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemSpecial }} <!---------------------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | == Solve "Special Telephony" Problem ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemSpecialFax }} <!------------------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | === Solve "FAX Transmission" Problem ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This problem type covers the following erroneous conditions:
| |
| − | :* FAX transmission doesn't start
| |
| − | :* FAX transmission is dropped
| |
| − | :* The transmitted document is incomplete
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Note |
| |
| − | If the FAX is connected to an IP-PBX then FAX problems must be solved with the responsible of the IP-PBX.
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | In a VoIP environment FAX no longer achieve the same degree of reliability as before in an analogue or ISDN one. The FAX reliability depends on various factors such as the type of device, device settings and the way the device is connected to the IP network. It depends also on the quality of the transmitter and receiver of the peer FAX devices. Getting all these factors together a transmission may not even start or dropped unexpectedly. The transmitted documents may be incomplete.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The users must expect increasing difficulties in the future, especially for international transmissions.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 1 | Check the FAX device configuration }}
| |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | e1=
| |
| − | Check:
| |
| − | :* the configuration of the FAX device
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Adjust the FAX device configuration:
| |
| − | ::* Reduce the transmission speed to max. 9600bds.
| |
| − | ::* Switch OFF the error correction as e.g. EMC
| |
| − | ::* If the device offers a "VoIP mode" then experiment with it and check if the results are better.
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 2 | Check the FAX transmission configuration of the gateway }}
| |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | e1=
| |
| − | Depending on the quality of the IP network the supporter and/or administrator of the gateway can experiment with the FAX transmission protocol of the gateway device.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Checks:
| |
| − | :* Check with the Telephony provider if there are recommendations or directives which type of FAX transmission protocols are to use, e.g.:
| |
| − | :** In band transmission with codec G.711alaw or G.711ulaw
| |
| − | :** Out band transmission with T.38
| |
| − | :* Check the configuration of the gateway device
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → If the user/customer has a good quality IP network and the Telephone provider allows it then try:
| |
| − | ::* "In band transmission with codec G.711"
| |
| − | :: → If the user/customer has a lower quality IP network and the Telephone provider allows it then try:
| |
| − | ::* "Out band transmission with T.38"
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{ToTop | SupportUserProblemSpecialDectMultiCell }} <!--------------------------------------------->
| |
| − | === Solve "DECT Multi-Cell with ISDN-PBX" Problem ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | This problem type covers the following erroneous conditions:
| |
| − | :* Hand over from cell to cell is not working
| |
| − | :* Bad speech quality
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Note |
| |
| − | If the DECT Multi-Cell system is connected to an IP-PBX then DECT problems must be solved with the responsible of the IP-PBX.
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | DECT-Multi-Cell systems connected to an ISDN-PBX which is working with in a VoIP environment experience special issues. Most issues are interconnected with accuracy of the synchronization clock of the ISDN-PBX. If this synchronization clock is not especially precise then the reference clock of the DECT-Multi-Cell system will have problems as described above.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Support_Step_Title | 1 | Check the ISDN reference clock }}
| |
| − | {{Support_3x3
| |
| − | |width1=725 | width2=75 | width3=75 <!--max 875-->
| |
| − | | e1=
| |
| − | Checks:
| |
| − | :* Does the ISDN-PBX take its clock reference from a high precision clock?
| |
| − | Actions:<br>
| |
| − | :: → Make sure the ISDN-PBX takes its reference clock from a high precision source.
| |
| − | :: → Use an ISDN-Gateway which provides a high precision clock.
| |
| − | :
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | Details of "RTP/RTCP" information collection: |
| | + | [[file:support_connection_rtp_rtcp_statistics_details_e.png |1000px|left|frameless| Dialog: "RTP/RTCP Details" ]] |
| | + | <br clear=all> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
The VoIP Switch administrators, operators and supporters find here information about the Session Initiation Protocol SIP and Session Description Protocol SDP.
Example of a "SIP dialog" with the minimal needed messages for a connection setup or connection renegotiation:
The SDP is embedded in the SIP messages during connection setup or connection renegotiation:
The Real Time Protocol RTP is used to transfer media data, e.g. speech in VoIP based telephony.
The Real Time Control Protocol RTPC transfers periodically statistical media data between the peers of a connection.
If RTP packets are lost, delayed or jitter then we speak of a Quality of Service QoS problem. For the support it is of interest to know if the number of transferred packets between the peers of a connection and if the numbers in the receive and send paths are reasonable equal, if packets were lost on call leg etc. With these statistical media information it can be possible to identify a path or transfer direction were QoS problems occure.